The Silicon Graphics Teaching Laboratory
has been replaced by the
Chemi
cal Information Laboratory
and this information is for historical interest only
Sybyl Notes
Mouse |
Top Menu |
Left Column |
Display Areas |
Function Keys |
Scripts
Sybyl is a general molecular modelling program written by
Tripos.
We are grateful to
GlaxoWellcome for donating a
licence to the Department of Chemistry.
Documentation (only available from SGTL machines)
To run the program, type sybyl.
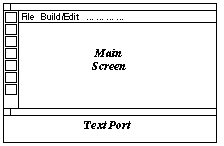
Mouse Buttons
The mouse buttons should be used individually or in pairs for the illustrated effects:
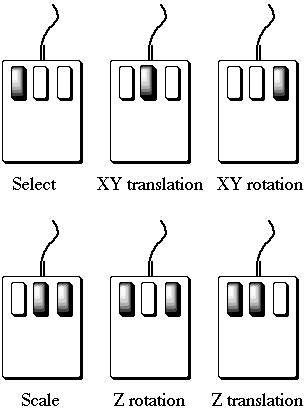
With the exception of scale, these operations can be performed on one or all
four (Global) of the display areas by swapping between them in the
normal way.
The Top Menu
The top bar contains a series of pull-down menus which contain all of the
building, viewing, and calculation routines in Sybyl. Beware that some
parts of the program require a separate licence to run.
If you require a routine that is not currently licenced to the Chemistry Department,
please contact Jonathan
Goodman.
For a brief summary what each menu contains, click on the appropriate key below.
Graphics Tools
The left column contains a number of gadgets that are extremely useful when
manipulating and viewing molecules. These are briefly summarized below.
 |
Advert for Tripos |
Also a variety of telephone numbers by which to contact Tripos, which
are useful for those who pay for telephone support
(The SGTL does not). |
 |
Display Areas |
Choose whether to manipulate all display areas (G for Global) or just one of D1, D2, D3, D4. |
|
 |
Screen Options |
Controls how molecules are displayed (ball and stick, spacefilled), the
screen format (quartered, full) and various stereo modes.
|
 |
Display Options |
This toggles molecules and backgrounds in the 4 display areas on and off.
The atom labels expecially useful. |
 |
Reset |
This resets rotations and translations in the display areas.
Unless a VIEW>FREEZE VIEW is issued, molecules can always be reset. |
 |
Rotate bonds |
Allows you to twist torsion angles. It is limited to 6 bonds per gadget,
but allows unlimited gadgets. |
 |
Z-Clip |
Controls Z-clipping. Pronounced "Zee-clipping" by the Americans. |
 |
Depth Cueing |
Controls depth cue. Default is 100% fading. |
 |
Windows |
Brings Sybyl windows to the front of the screen |
 |
Stereo |
Controls spacing between molecules when in stereo mode. |
 |
Physical dial box |
This is not useful unless you have a physical dial box. |
 |
Virtual Dial Box |
Acts much like the Alchemy rotation/translation controls. |
 |
Rate mode |
Excellent for hands-off molecule rotation. Good to impress management. |
| OPTION |
Description |
| Read |
Reads molecules in various formats. Sybyl standard format is .mol2 |
| Save As |
Writes molecules and suchlike. Both .mol2 and .pdb formats |
| Database |
A file containing multiple molecules. Good for organizing projects. |
| Molecular spreadsheet |
Sybyl's spreadsheet - can accept molecules in cells |
| Log commands |
Saves commands as a macro |
| Take commands... |
Reads a macro ("take" file in Sybylspeak) |
| Log session |
Records commands during a session |
| System Window |
Allows the user to issue UNIX commands. Type "exit" to return to Sybyl. |
| Plot |
Postscript or HPGL |
| Exit |
Vaya con dios |
| Undo |
Undo last action. All is not lost... |
| Zap molecule |
Deletes one or more molecules |
| Get fragment |
Gets molecular fragment from Sybyl's library |
| Sketch molecule |
Sybyl's sketching tool. The fastest way to build a molecule |
| CONCORD/SMILES |
Converts from SMILES to 3-D. Requires a CONCORD licence. |
| Clean-Up |
Performs a torsional hunt or rough dynamics. |
| Name molecule |
Most molecules answer to "Fred". |
| Center... |
Centres the molecule on one or more atoms. |
| Copy... |
Copies a molecule from one molecule area to another |
| Merge... |
Combines two molecules into one molecule area |
| Extract |
Copies a part of a molecule into another molecule area |
| Aggregates... |
Fixes part of a molecule for purposes of minimisation. |
| Constraints... |
Applies bond stretch, angle, and torsion constraints. |
| Add |
Adds atoms, bonds, etc. |
| Define |
Defines sets, centroids, normals and planes |
| Delete |
Deletes atoms, bonds, etc. |
| Modify |
Modifies atoms, bonds, atom types etc. (Necessary for good force field results) |
| Other Tools |
Chirality and fusion tools |
| Crystals |
Crystal structure viewing options. |
| Solvent |
Solvation options. |
| Color |
Colours molecules, atoms, bonds or labels. |
| Display Atoms |
Selectively displays atoms or monomers... |
| Undisplay Atoms |
...and then hides them. |
| Label |
Selectively labels atoms, bonds, or substructures, by ID or type... |
| Unlabel |
...and then hides the labels. |
| Center of Rotation |
Allows the user to change the centre of rotation. |
| Freeze view |
Freezes molecules in current orientation/location. Necessary after docking. |
| Delete all backgrounds |
Deletes all backgrounds |
| Background |
Reads, writes, lists, and changes the colours of backgrounds |
| Annotation |
Puts labels, arrows and titles onto screen. |
| Rendering Options... |
Controls the Display Options gadget in left hand column. |
| Mixed Rendering... |
Creates a spacefilled, ball-and-stick, or stick version of the molecule. |
| Dot surfaced |
Creates a vdW or Connoly dot surface. |
| Contour surfaces |
Creates volume or isopotential surfaces. These are large files. |
| Shaded surfaces... |
Apply shading to a previously calculated surface. |
| Display H-Bonds |
Creates a static or dynamic display of hydrogen bonds. |
| Monitor |
Dynamically updates distances and hydrogen bonds during manipulation. |
| Constraints |
View constraints added previously. |
| Ruler |
Add a ruler to the display window |
| 2D Viewer |
Converts molecule to 2-D structure |
| Backdrop |
Changes backdrop style |
| Minimize... |
Minimizes using the Tripos or Kollman (AMBER) force fields. |
| Minimize subset |
Minimizes only a portion of the molecule. |
| Dock |
Perform a docking simultion. |
| Energy |
Computes the energy of a given molecule. |
| Multifit |
Fits two molecules together with energy minimisation. |
| Superimpose |
An alternate method of fitting. Can also fit on electrostatic fields. |
| Charges |
Calculates atom-centred charges using a variety of algorithms. |
| Dipole... |
Calculates the magnitude and direction of a molecular dipole. |
| Force field parameters |
Add,view, or modify parameters. |
| Multiple DG Embedding... |
Specifies bounds for distance geometry simulations. |
| Distance Geometry |
Uses distance geometry to do a conformational search or docking. |
| Molecular mechanics |
Minimisation using the MM2 force field. |
| Dyamics |
Menus to set up molecular dynamics and simulated annealing simulations. |
| BOSS |
Monte Carlo simulation or free energy perturbation. |
| Search |
Torsional searches : grid, random, or systematic searches. |
| AutoCOMFA |
Interface to COMFA routines. This requires a COMFA licence. |
| Interfaces |
to MOPAC, ZINDO, EHMO, Gaussian, CCDC, Medchem, and DGEOM (not all available). |
| Netbatch |
Distributes jobs among a group of computers. |
| Measure |
Measures distances, angles, torsions and suchlike. |
| Match |
Overlays molecules. Atom matching is in order chosen. |
| Fit atoms |
Also overlays molecules. Requires pairwise picking of atoms. |
| Superimpose... |
Superimposes two molecules. |
| Distance Geometry |
Analysis of DGEOM results. |
| Molecular Mechanics |
Analysis of MM2 minimisations. |
| Dynamics |
Analysis of MD simulations. |
| BOSS |
Analysis of BOSS simulations. |
| Search |
Analysis of conformational searches. |
| Interfaces |
Analysis of other calculations. |
| Set |
Changes defaults. Try SET BOND 3 to improve graphics on some terminals. |
| Tailor |
Changes defaults for many calculations and routines. Check the menu for details. |
| QSAR |
Sets up a molecular spreadsheet with QSAR options. |
| Biopolymer |
Opens a peptide building and analysis menu. This appears on the Top Menu. |
| Info |
Lists molecular information. |
| List |
Lists other useful information. |
Top Menu : Biopolymer (Choose from "Options" Menu)
| Build |
Builds proteins, nucleic acids or carbohydrates. |
| Brookhaven File |
Reads or writes .pdb format files. |
| PIR File |
Reads or writes PIR format protein sequence files |
| Add Hydrogens... |
Adds hydrogens to a protein structure |
| Add Sidechains... |
Builds sidechains onto a protein backbone trace |
| Load charges |
Loads atom-centred charges from a sidechain library |
| Conformation |
Tools to measure and set protein conformation |
| Modify |
Tools to delete, insert and mutate protein residues |
| Fit Monomers |
Fits two protein chains |
| Find and Fit Fixed Regions... |
Automatically fits similar regions. Useful for homology modelling. |
| Analyze Protein (ProTable) |
A useful protein analysis tool. Requires a separate licence. |
| Display |
Ribbon and tube tracings of protein backbone. |
| List sequence... |
Lists a protein sequence. |
| Align sequences... |
Sequence alignment tool. |
| Predict secondary... |
Predicts the secondary structure of a protein sequence. |
| Search protein database |
Searches a proprietary version of the Brookhaven database |
| Protein Loops... |
Homology modelling tool for protein loops. |
| Monomer dictionary.. |
Provides access to the dictionary of monomers. |
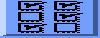
Display Areas
Sybyl has four display areas: D1, D2, D3, D4. The default setting is G (global),
and this means that rotations, translations, etc will apply to all the
molecules. By clicking the Display Area button, you can choose a particular display area to manipulate. The Display areas may be superimposed, or quartered around the screen in the order shown in this figure:
To control whether or not to have quartering, use the
Screen Options button.
Molecular Areas
Whenever you read a molecule from a file, or start drawing on the screen,
you will be asked which molecular area you want to use. The name of
each area is M#, where # is a number. The work area name associated with a
molecule does not change during a session. If you are working with several
molecules, you can distinguish them by their molecular area name.
The Molecule Areas are associated with Display Areas in the following manner:
- D1 : M1, M5, M9, M13 ...
- D2 : M2, M6, M10, M14 ...
- D3 : M3, M7, M11, M15 ...
- D4 : M4, M8, M12, M16 ...
Backgrounds and Backdrops
Background displays are graphical information other than the molecule itself. These include the various types of surfaces and other images that Sybyl can create. These images are attached to a particular display area and respond to rotations, translations, etc just like any molecule in the same display area.
A Backdrop is the colour or image behind the molecules and backgrounds. By default, this is black, but can be changed to other colours or patterns using the Backdrop option of the View menu.
Function Keys
|
F1
Hides the text window. Press F1 again to toggle back.
F5
Toggles between photo and normal display modes.
F6
Toggles toolbox icons on and off.
F7
Toggles hardware stereo on and off.
F8
Raises or lowers graphics window, when hardware stereo is active
|
F9
Toggle between D1 and G
F10
Toggle between D2 and G
F11
Toggle between D3 and G
F12
Toggle between D4 and G
|
- Cursor left
- Rotate +90 degrees around the y-axis
- Cursor right
- Rotate -90 degrees around the y-axis
- Cursor up
- Rotate +90 degrees around the x-axis
- Cursor down
- Rotate -90 degrees around the x-axis
- Ctrl
- Hold down Ctrl in combination with a left mouse click
to select a molecule or background for object transformation.
|
Scripts
Sybyl has a powerful scripting language.
An archive of
Sybyl scripts is available from the Rennselear Polytechnic Institute.
Information on
Graphics, including how to change the colour of the screen (backdrop) is available from Tripos.
|